Modifying the mobile phone system sounds extremely complicated if you do it yourself. However, with the help of some tools and scripts, ordinary users can also achieve deep customization effects, such as streamlining pre-installed applications or adding new features.

Unpack image file
Load the IMG image file of the mobile phone firmware. This is the first step to modify the system image. You need to prepare a ROM assistant tool for this. Then release all the files in the system partition to your computer's hard drive, a process that allows you to directly access and edit them. During the unpacking operation, select the corresponding IMG file in the software interface, click the unpack button, and wait for the progress bar to complete. Afterwards, you can see the complete system file structure in the output directory.
After the unpacking is complete, you can start streamlining the system. The most common method is to delete the applications that exist with the operator or are pre-installed by the mobile phone manufacturer. These APK files are usually in the directory range of /system/app or /system/priv-app . Before deleting, it is best to make a backup first and clearly confirm that these applications will not affect the core functions of the system. By deleting unnecessary applications, you can make space for the system partition or make the system run more smoothly.
Editing and modification system
Go into the unpacked folder and you will have all the permissions to make changes to the system. In addition to deleting the app, you can also replace the system font, ringtone, or startup animation. These resource files are located in /system/fonts , /system/media and other paths. When replacing, please note that the file format and permissions remain the same as the original file to prevent the system from recognizing it.
Deeper modifications are related to the deployment of system parameters. You can edit the /system/build.prop file to change the phone model identification, or adjust the screen density, or enable hidden functions in the developer options. Such modifications have certain risks. Inappropriate changes may cause the phone to fail to start. It is recommended to only modify one parameter at a time, and keep a record after modification for easy traceability.
Repackage the image
After completing the modification, the scattered files must be repackaged into an IMG image. Tools used for packaging generally provide several parameters. For example, the -s parameter can compress the image and remove unused blank space, thereby making the final generated file smaller. The -T parameter allows you to set a specific modification timestamp for the image file.
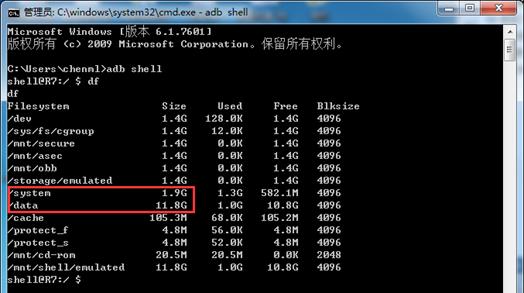
The entire packaging process has a very strict limit on the partition size. You have to use the -l parameter to specify the upper limit of the image size. Its unit is megabytes, which is M. This value must be slightly larger than the original actual total size of all files, but it must not exceed the capacity of the original partition. If the packaging process fails and a prompt is given indicating that the image is too large, then you have to go back and delete more files or adjust the parameters.
Batch script automation
If you perform manual operations, the process is complicated, trivial, and error-prone. However, if you use a batch script to do it, you can greatly improve the efficiency. For the Android 4.4 system, the script can automatically complete the process of placing the APK and its supporting library files, that is (.so files), into the directories /system/app and /system/lib respectively. You just need to place the application files to be integrated in the specified folder and then run the script.
A more complex system has appeared on Android 5.0 or 5.0, and the logic of the script must also be adjusted. The new system requires that the APK and its library files must be placed in the same subdirectory. The script must first create a folder named according to the application package name, then move the APK and lib files into it, and finally copy the entire file to the system application directory. The script can also handle special restrictions such as the application name cannot contain Chinese characters.
make_ext4fs -S file_contexts -s -l 3072M -a system system.img ./system
Advanced features of scripts
A mature script should cover more practical functions. For example, it can automatically extract essential library files from APK files. Since the command line tools of commonly used compression software do not support the APK format, the script may need to call the command line interface provided by domestic software such as "Haoyi".
In addition to being interactive and adaptable, the script also prompts the user to make a choice between installing the application on the /system partition or the /data partition, which can meet the needs of different machine models. At the same time, the script can automatically read the size limit of each partition of the phone to ensure that the packaged image does not exceed the standard, thereby avoiding failure during the flashing process due to lack of space.
Notes and interactions
Before starting the modification, be sure to use the ADB command "adb pull" to extract the key original system files from the phone for backup, such as "/system/build.prop". During the entire process, patient and careful recording is extremely critical. Neglecting any step may cause the phone to become bricked. Have you ever had the experience of customizing your mobile phone system? What was the biggest challenge encountered in the process? Welcome to share your experiences and thoughts in the comment area. If you find this article helpful, please give it a like and support.