Opening a port on the server seems to be quite simple, but if it is not configured properly, it is very likely to directly cause the service to be inaccessible, or bring security risks.
Understand firewall inbound rules
The security barrier between the computer and the external network is the firewall. Rules control the entry and exit of data into the firewall. Externally initiated connection requests are specifically managed by inbound rules. Inbound rules determine whether access to specific ports on the local machine is allowed. The basis of Web services is to open port 80. Blindly opening all ports will introduce hidden dangers. The key to balancing functionality and security is to configure rules appropriately.
Each rule is similar to a door. It needs to be clear who can enter, from where, and to where. Firewalls in modern operating systems often have graphical interfaces and advanced configuration options, allowing users to conduct refined management. Understanding the basic logic of these rules is a prerequisite for any port configuration.
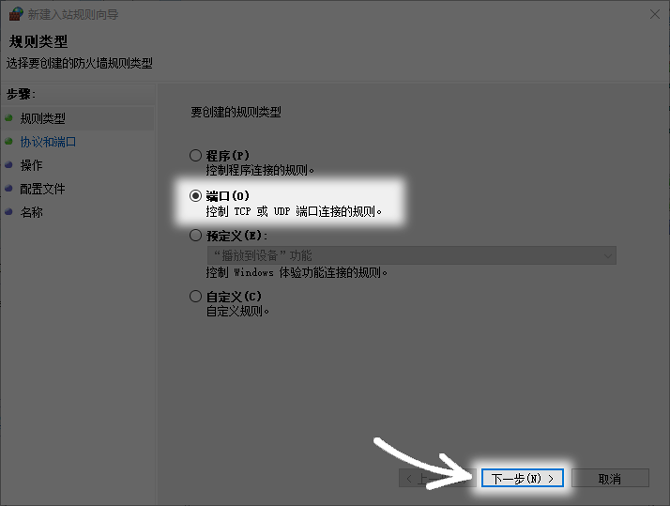
Choose the right rule type
When creating a new rule, the system will give you several types, such as "Program", "Port", "Predefined" or "Custom". For open web services, the "port" type should be selected. This means that the rules will take effect directly on the network port instead of being associated with a specific application. In this way, even if the service is restarted or the software is changed, the rules will still be effective.
If the "Program" type is selected incorrectly, the rules will be bound to a specific .exe file. Once the program path is changed or upgraded, the original rules will become invalid. Port rules are more versatile and stable and are the preferred way to configure network services.
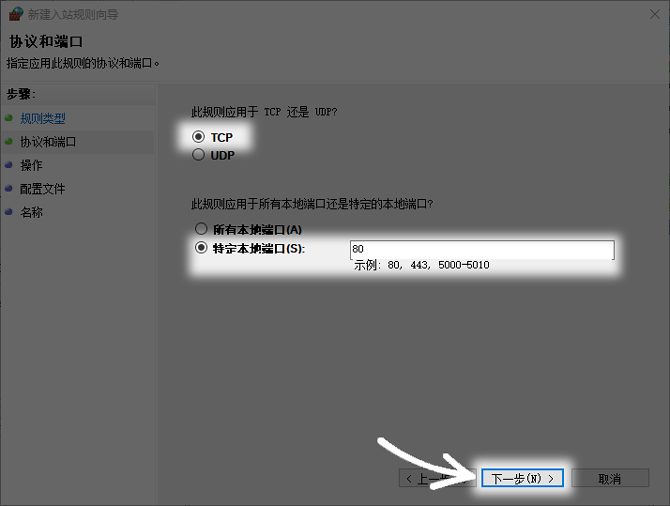
Configure protocol and port number
In the future, you need to specify the protocol and port number. Common transport layer protocols include TCP and UDP. Web services generally use the TCP protocol. In view of its ability to ensure reliable and orderly data transmission, port number 80 is the international standard port for HTTP services. When setting up, you should accurately select the "TCP" protocol and enter "80" in the "Specific local port" column.
If there is a need to open multiple ports at the same time, you can use commas to separate them, like "80,443". You can also use hyphens to represent ranges, for example "8000-8010". If there is an error in the protocol selection, such as selecting UDP for the Web service, the connection will not be established.
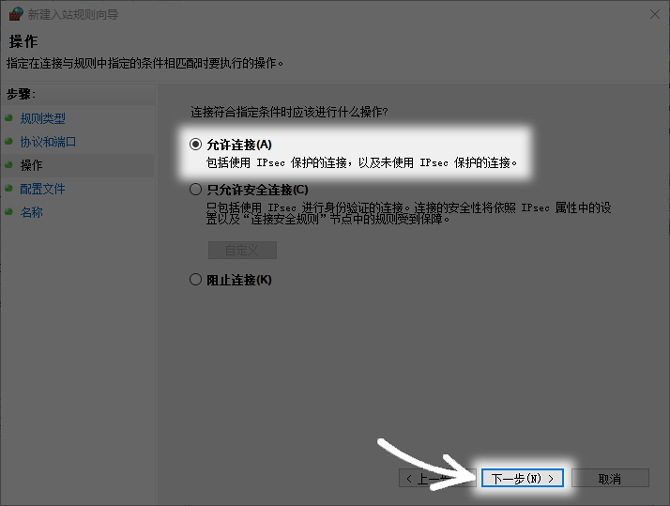
Set allowed connection operations
The core operation is to determine how the firewall handles connection requests that meet this rule. There are three options available here, namely "Give connection permission", "Only allow secure connections" and "Block connections". For general network servers, this can be achieved by selecting "Give connection permission". This option will allow all incoming traffic that meets the protocol and port conditions to be allowed.
Restricted to only allowing secure connections, this requirement stipulates that connections must be encrypted by IPsec and authenticated, and is applicable to intranet environments with extremely high security requirements. Blocking connections has the opposite effect. You must be sure to choose the correct operation, otherwise the rules will lose their due meaning.
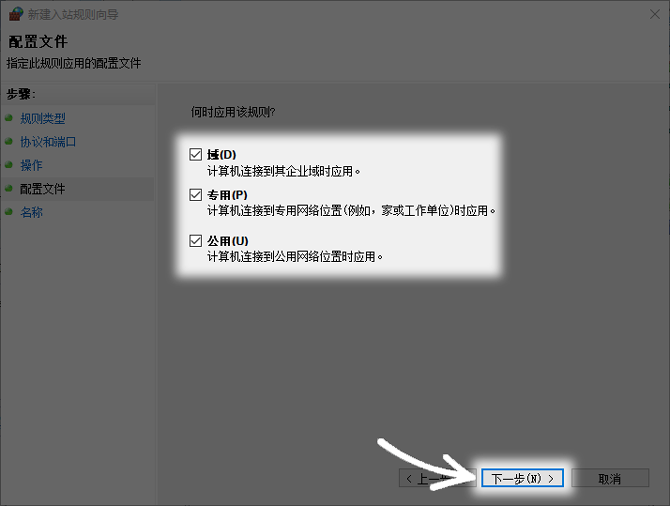
Apply rules to network configuration files
System networks are often divided into three types: domain networks, private networks, and public networks. What it calls "domain network" refers to the kind of internal environment that is managed by a company's domain controller. A "private network" refers to a trusted network such as a home or office. As for "public networks", they are networks where there are insecurities such as coffee shops and airports.
In order to ensure that Web services can be accessed in various network environments, it is recommended to apply this rule to three network configuration files. If the server is only used on the intranet, you can only check "Domain Network" and "Private Network" to reduce the risk of exposure to public Wi-Fi.
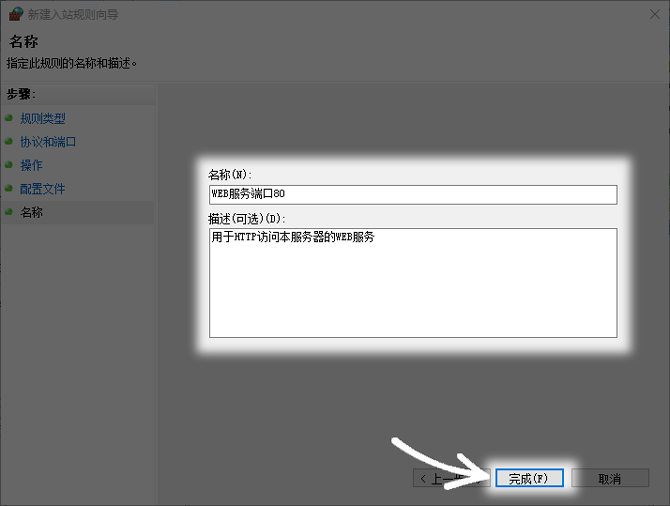
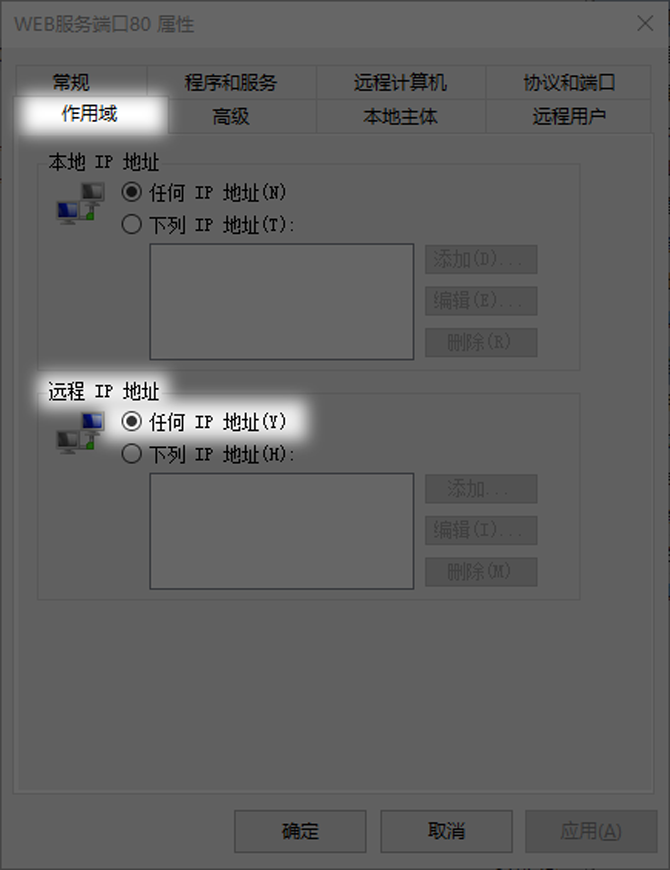
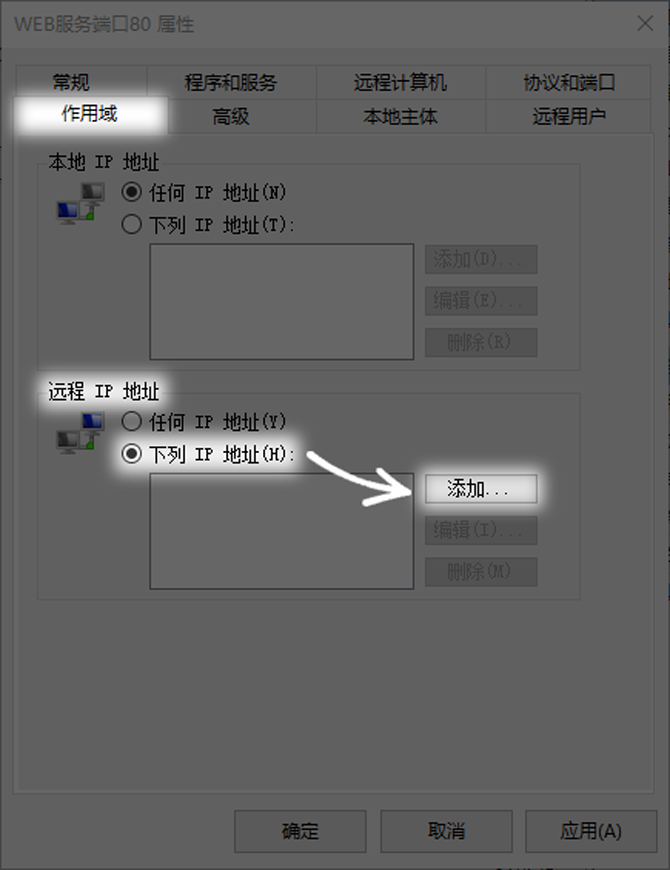
Refine rule scope and save
After creating the basic rules, you can further restrict the source of access. In the "Scope" tab of the rule properties, you can set the "Remote IP Address". The default "Any IP Address" means that devices within the entire Internet can try to connect to your 80 port.
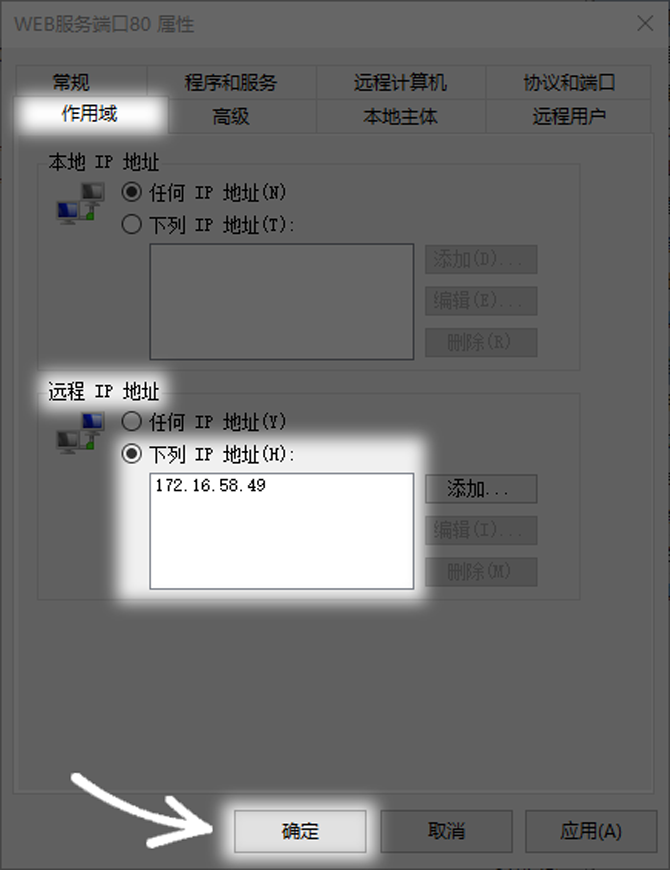
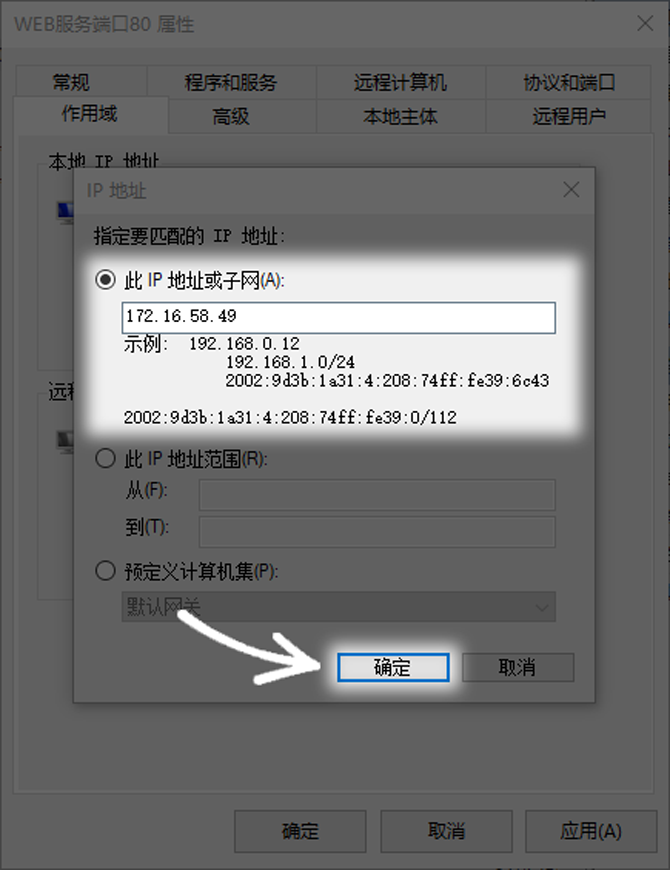
In order to improve security, you can change it to "the following IP addresses" and then add a single IP or IP segment that is allowed to access. For example, if the server is only for internal use of the company, you can enter the IP address range of the company network, like 192.168.1.0/24. In this way, only requests originating from this network segment will be allowed, which greatly reduces the attack surface.
For the sake of convenience, when configuring firewall rules, would you prefer to open all IPs, or for the sake of security, would you strictly limit the source IPs? You are welcome to share your experience and opinions in the comment area. If you find this article useful, please like and support it.




