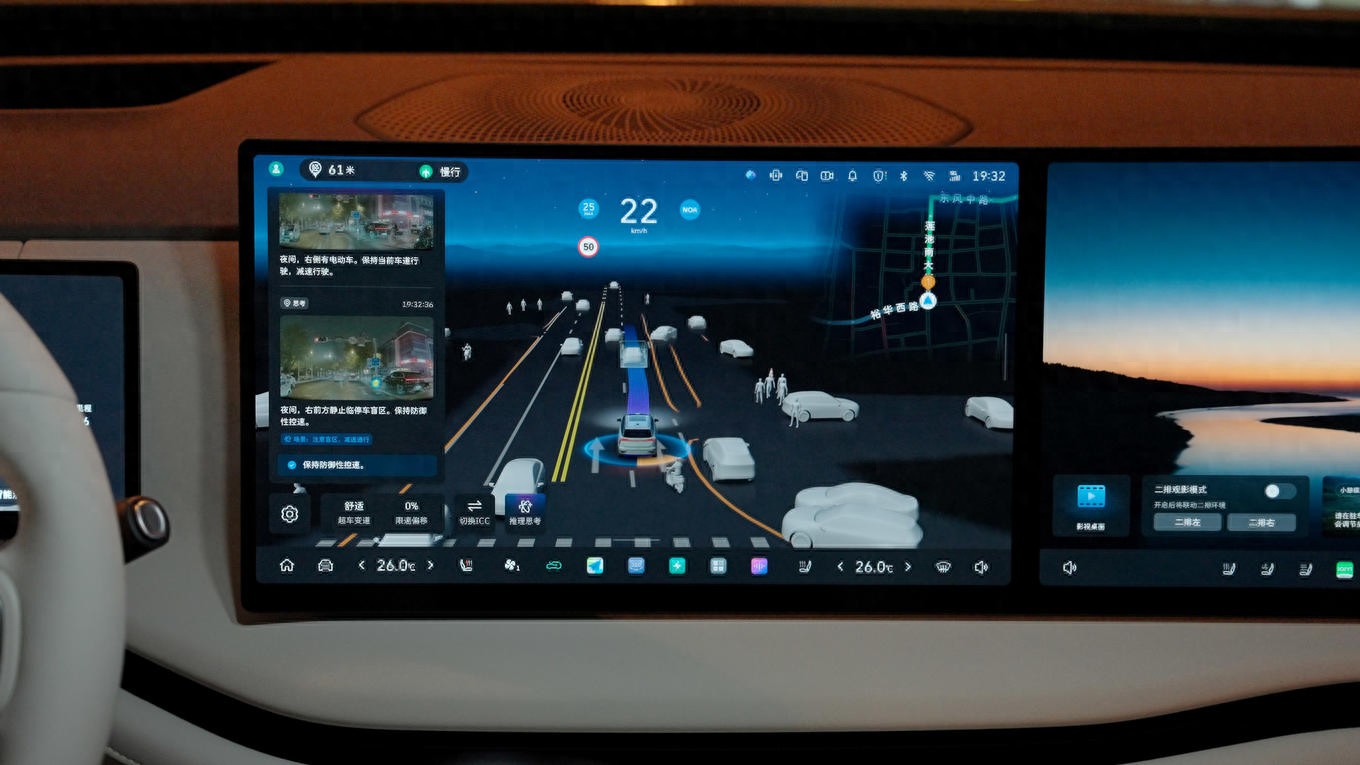
The ongoing competition for assisted driving is changing from a competition of massive accumulation of hardware to a competition of "thinking ability". Great Wall Motors has incorporated large-scale model technology derived from robots into mass-produced vehicles. Can this situation make vehicle driving more human-like?
Fundamental changes to the underlying logic
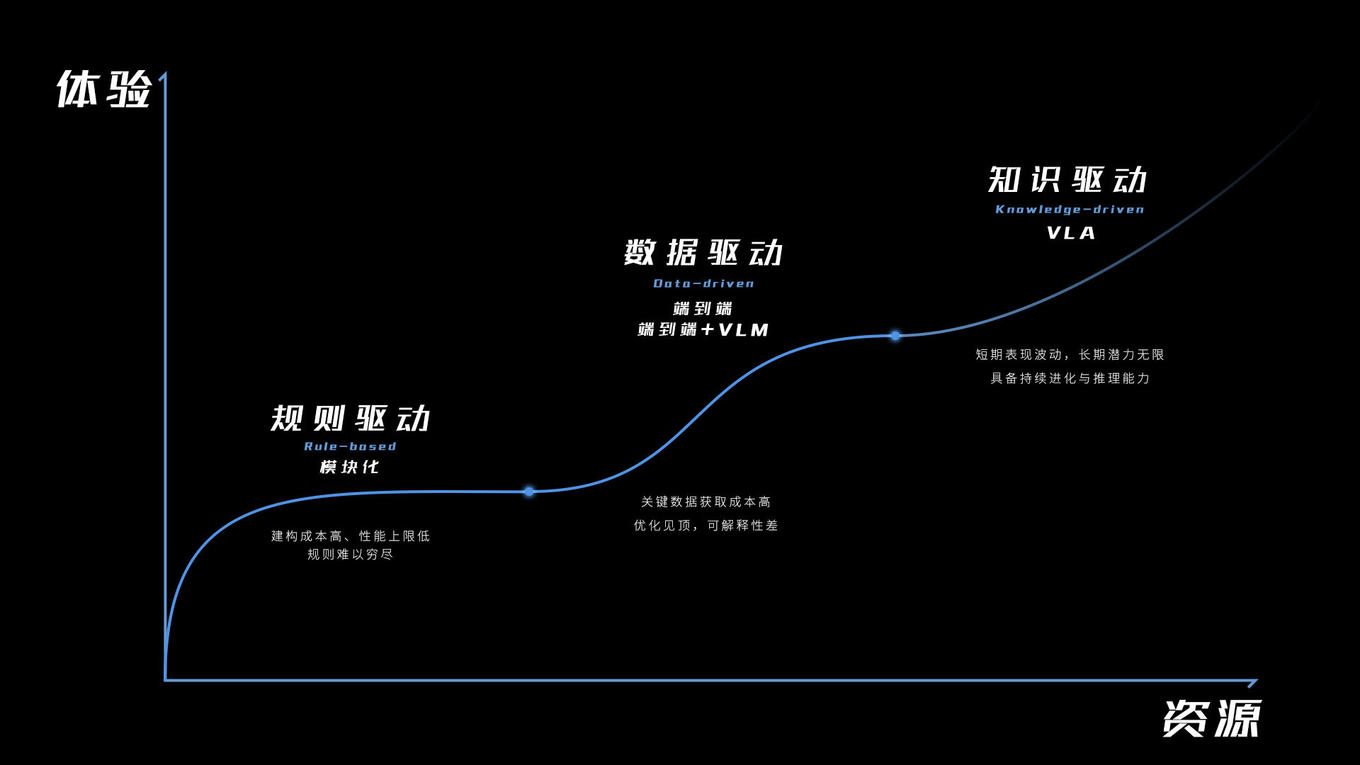
Relying on preset rules and a large amount of data annotation to identify objects and then react, this method is used by traditional assisted driving systems. When encountering "long-tail scenarios" that are not covered in the training data, it is easy to appear rigid or even ineffective. The core of the VLA model introduced by Great Wall Motors is to imitate the human cognitive chain.
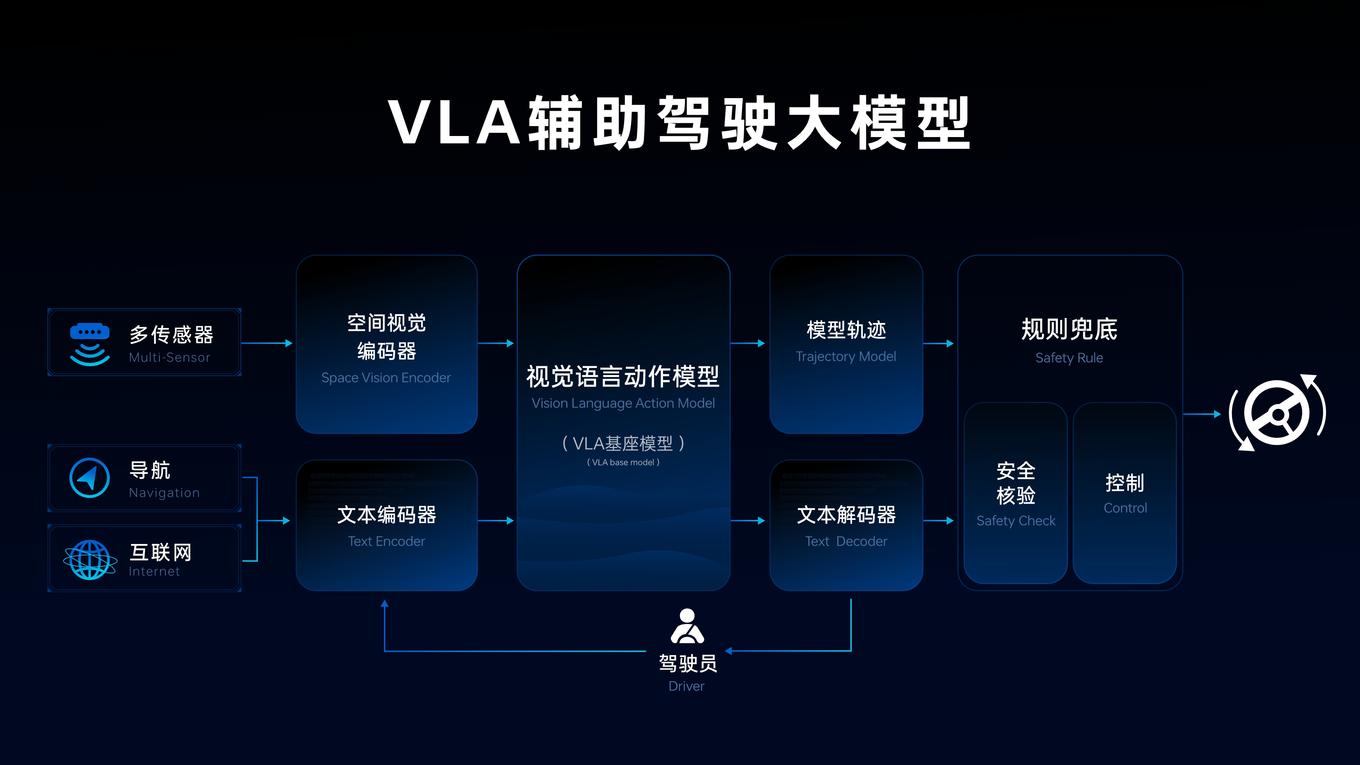
It attempts to make the vehicle first "see" the surrounding environment like a human being, then "understand" the semantics and potential risks in the scene, and finally "infer" appropriate driving actions. This transition from "perception-execution" to "perception-understanding-reasoning-execution" is an extremely critical step in dealing with complex urban road conditions.
From abstract ideas to concrete actions
The primary goal of all assisted driving systems is safety. However, how to convert abstract "safety" into specific operations of the machine has always been a problem. To address this problem, Great Wall Motors' new generation CP system came into being. This system is a product that combines the risk judgment capabilities of the VLA large model with vehicle control execution.
The VLA is responsible for carrying out environmental understanding and risk assessment in the background, and then forming decision-making recommendations. The CP system is responsible for accurate execution, converting the recommendations into specific operations such as acceleration, deceleration, and steering. This is like equipping the vehicle with a "co-pilot" that continuously performs risk deductions and programs defensive driving strategies.
A driving assistant that understands human speech

In the new Blue Mountain Smart Advanced Edition, users can directly communicate with the assisted driving system using natural language. Instructions such as "Help me start", "The intersection ahead is too complicated, be careful", or "Stay away from the large truck next to you" must be accurately understood and executed safely by the system.
To achieve this goal, the system must not only have powerful speech recognition and semantic understanding capabilities, but also must combine real-time visual perception to determine the feasibility and safety of the command. For example, when the user says "stay away from big cars", the system needs to identify the surrounding giant vehicles and plan a safe route away from them.
Coping with complex urban scenarios
Public actual tests carried out in Baoding, where Great Wall Motors is headquartered, showed that the new system showed different strategies when faced with typical urban scenes. When encountering temporarily parked vehicles or construction barriers on the roadside, the system would slow down appropriately in advance and try to "probe" to observe the road conditions in the blocked area just like a human driver.
For the system, after confirming that the opposite lane is in a safe state, it will carry out a small detour. When following a large vehicle through an unprotected intersection, the system will become more cautious due to the obstruction of the line of sight, which will extend the time for observation and judgment, rather than blindly following the vehicle in front.
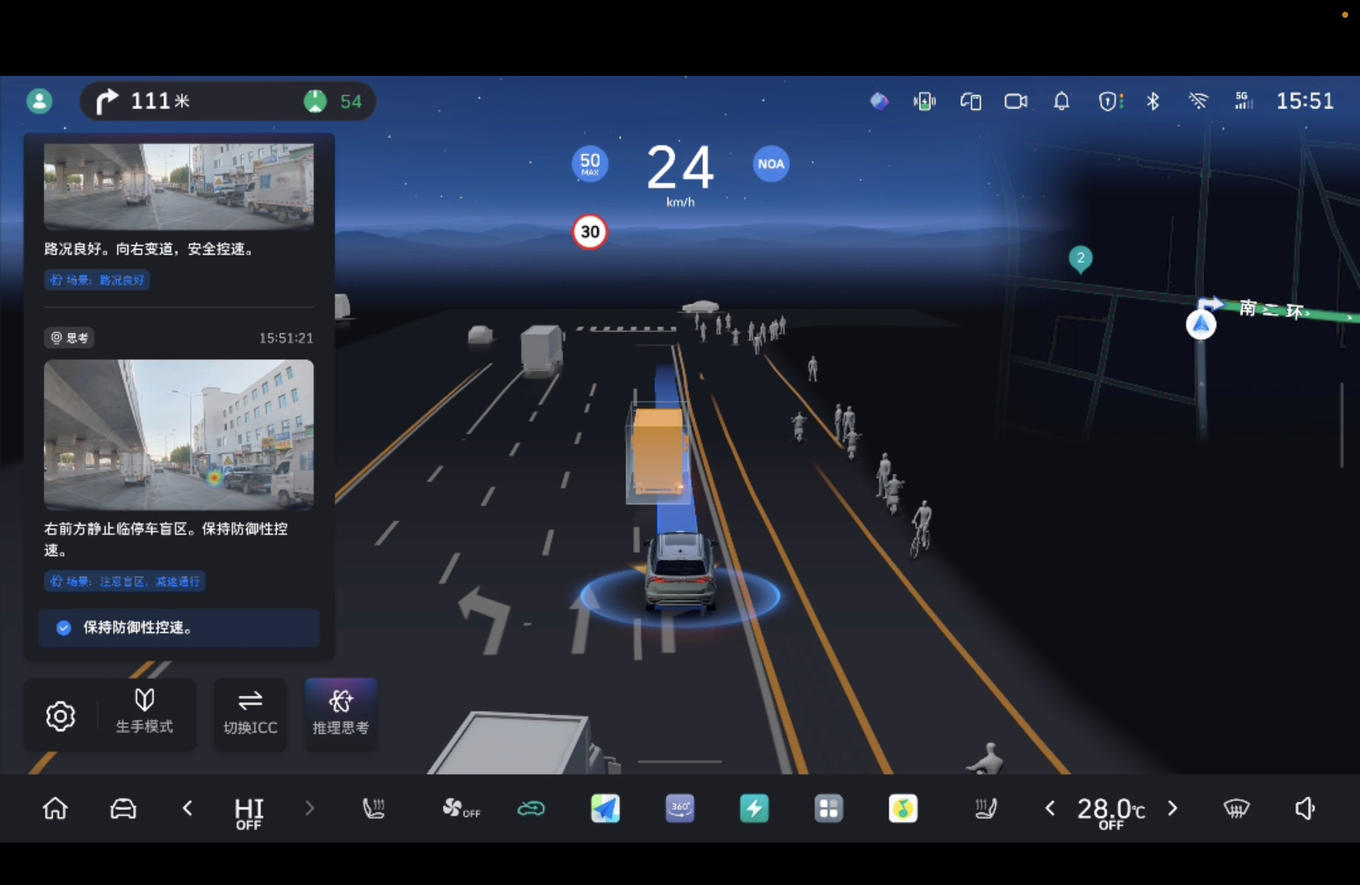
A visual window to build trust
To allow users to understand "why the machine drives itself like this", Great Wall Motors has added a visualization function of the decision-making process to the CP system. The vehicle's central control screen will dynamically display the system's current "thinking context".
For example, the cards will be displayed one by one, first "perceiving a stationary vehicle on the right", second "inferring that there may be a risk of 'opening the door to kill'", then "decision to fine-tune the direction to the left and slow down", and finally "executing avoidance". Such a transparent presentation aims to eliminate users' doubts about "black box operations" and is a key bridge to build trust between humans and machines.
Hardware redundancy and future expansion

The hardware of the new Blue Mountain Smart Advanced Edition has been upgraded, equipped with 27 sensors, and uses a new high-computing power chip, resulting in a total computing power redundancy of 176%. The basic guarantee for the VLA large model to be able to perform real-time, full-link calculations is its powerful computing power.
Great Wall Motors claims that the Blue Mountain model is only the beginning of the mass production application of VLA and CP systems. In the future, this technology will continue to expand its capabilities through the installation of more new models and OTA upgrades of existing vehicles to cover more diverse and complex real road conditions.
For people at the consumer level, will an assisted driving system with the ability to "think" and "communicate" and a driving style more similar to that of experienced drivers become the most important factor when you choose a smart car? You are welcome to share your opinion in the comment area whether such an assisted driving system will become the most important factor when purchasing a smart car. If you feel that this article is helpful, please support it by giving it a like.




