Android phones running memory cleaning tools, as well as video processing and editing tools, are facing the same thorny problem: many old versions of applications, due to the tightened access rights of the operating system, are unable to conduct deep scans of the phone's storage data space, making it impossible to achieve deep cleaning. The latest version of the application platform created using new technological innovation solutions is expected to reverse such an unfavorable situation.
Core principles of technical solutions

This solution avoids the traditional path of obtaining the highest permissions via ROOT. It relies on the legal debugging channel reserved for developers by the Android system, that is, ADB permissions. With this channel, the application can obtain higher file system access rights than during regular installation.
This situation is similar to that of Windows systems, where some programs are run as "administrators." On the Android side, this process requires the user to manually authorize pairing. After authorization is completed, the application can read deeper directories in the user's storage, such as the "/data" area that contains application cache data.

The practical convenience brought by ROOT-free

For the vast majority of users, the ROOT operation is complicated and risky. It will cause the phone to lose its official warranty. Improper operation may also cause the system to crash. The ROOT-free solution completely avoids these worrying aspects.
First, the user must complete a one-time authorization action in the settings, and then the application can run normally. This shows that users do not have to crack the mobile phone system for deep cleaning. While maintaining the integrity of the system, they can obtain almost ROOT-level file management capabilities. This is particularly effective for managing duplicate files created by dual-open applications.
Dramatic improvements in scanning speed
Previously, the scanning speed of the tool was slow, partly due to insufficient permissions, which required repeated searches within a limited access scope. After obtaining a higher level of access permissions, the application can directly locate the target folder, greatly reducing the time spent on path retrieval.

Especially when scanning social applications that generate a large amount of cache, such as WeChat and QQ, the perception brought by the speed improvement is very significant. In the past, a full scan might have taken several minutes, but now it can be completed in tens of seconds. It can also accurately list the cache files that can be cleaned, thus improving usage efficiency.

Extended support for SD card and application dual opening
In addition to targeting the built-in storage of mobile phones, this solution also extends management rights to external SD cards. Many users have the habit of transferring photos and videos to SD cards. The new version of the tool can effectively scan and clean redundant files in these mobile storage devices.
At the same time, it has been specifically optimized for the identification of the "double-open application" or "application clone" directories. The system creates an independent storage space for the clone application, which is often missed by traditional cleaning tools. The new solution can scan the data directories of the main application and the clone application at the same time to ensure that there are no dead ends in cleaning.
Specific activation steps
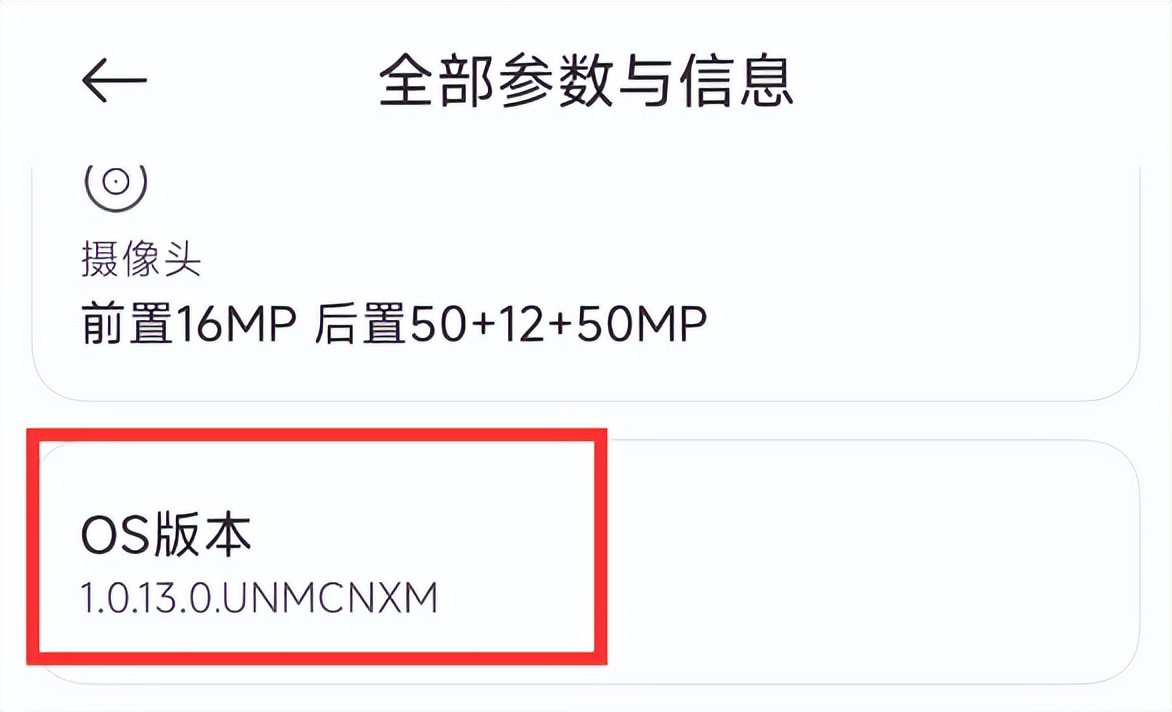
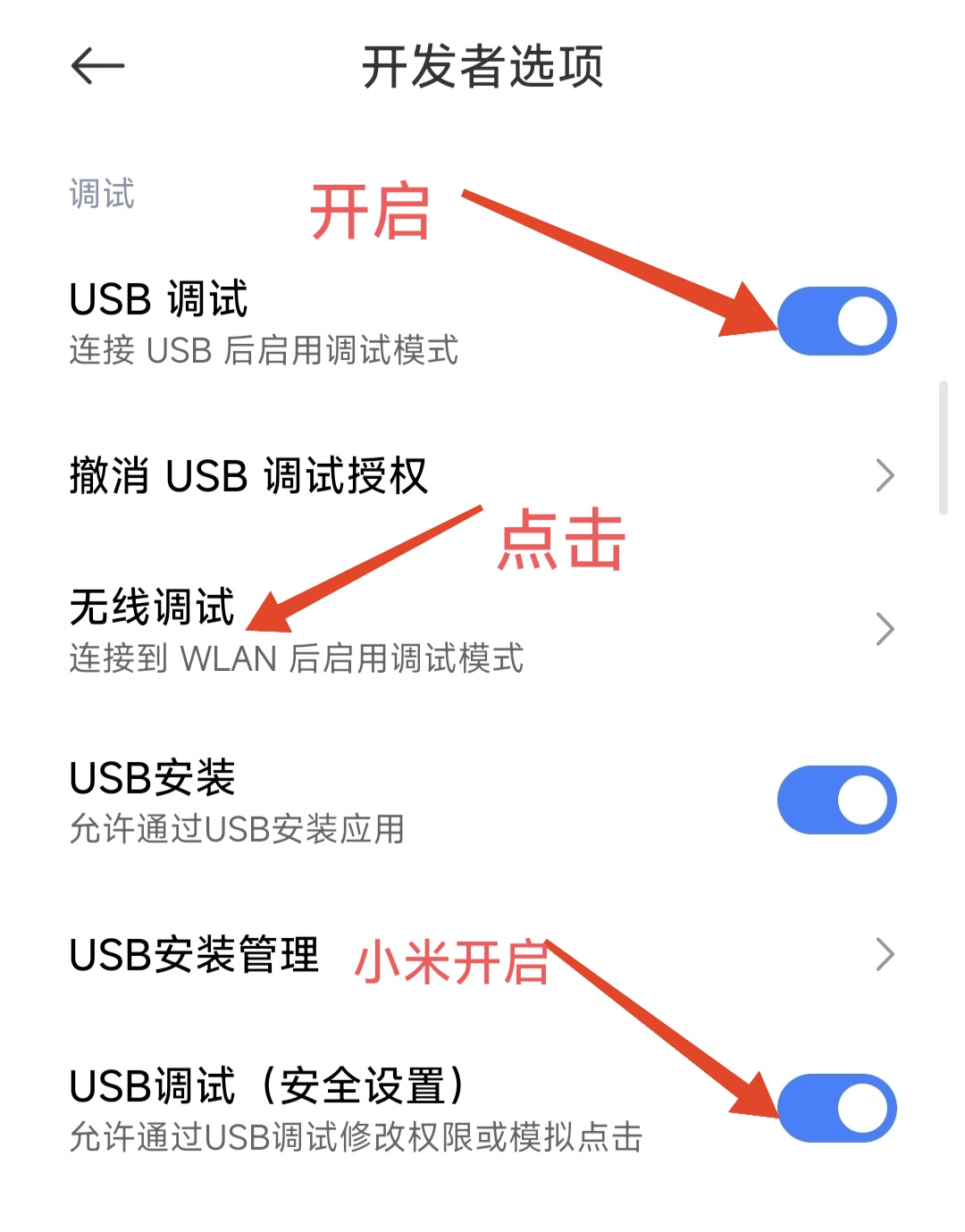
The entire activation process is centered around turning on "Developer Options" and performing wireless debugging pairing. The first step for users is to enter the phone settings, then look for "About Phone" or a similar menu, and then click "Build Number" more than 7 times in a row until they see a prompt that the developer mode is turned on.
Afterwards, return to the main settings menu and look for the newly popped up "Developer Options". After entering, turn on the "USB debugging" function, find the "Wireless debugging" option and enter the pairing page. At this time, the phone screen will display a six-digit pairing code, an IP address and a port number.
Frequently Asked Questions and System Differences
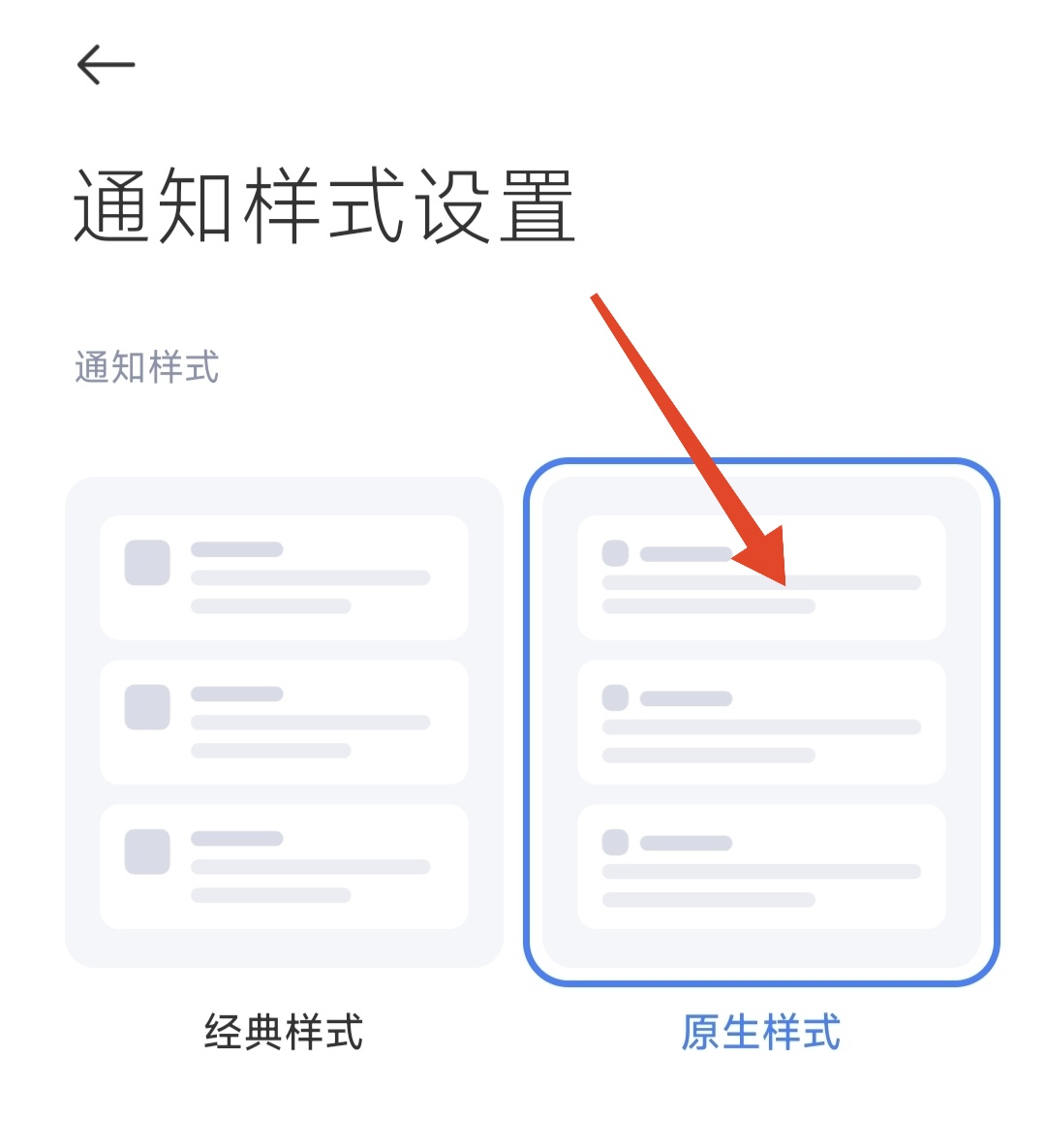
The difference is that the operation interfaces of different mobile phone brands are different, and the option names are also different. For example, for Xiaomi phones, you have to turn on the "USB debugging (security settings)" and adjust the wireless debugging notification style to "native style" so that the pairing code input box can be displayed normally.
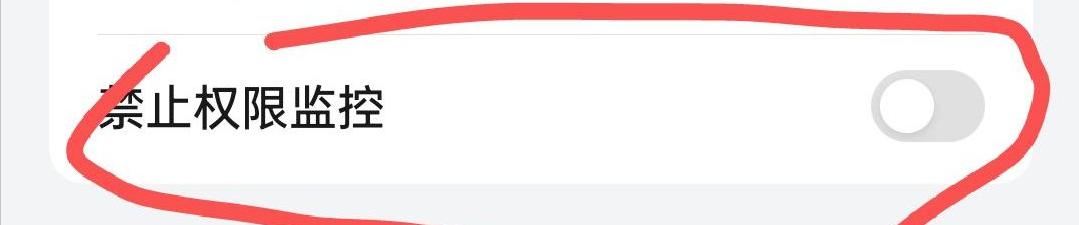
For mobile phones of some brands, such as OPPO, OnePlus, Realme, etc., you may have to find and turn off the "Permission Monitoring" function at the bottom of the developer options. However, Huawei and its Hongmeng system cannot use this method since they do not have integrated wireless debugging functions. They must connect to a computer and execute ADB commands to achieve authorization.

After pairing and activation are completed, the app can use all its functions normally. It should be noted that do not turn off the developer options and USB debugging switch. After the phone restarts, you usually only need to click "Reconnect" once in the application, and there is no need to repeat the entire pairing process.
Have you ever been troubled by insufficient storage space on your phone? Have you tried other cleaning tools? Welcome to share your experiences and opinions in the comment area. If you think this article is helpful, please like it to support it and share it with more friends.