In the past few years, the field of design rendering has been undergoing a revolution. The adoption of placing rendering tasks in the cloud for processing has gradually begun to change the workflow of many designers.
The core principles of cloud rendering technology
Traditional rendering work relies on the computing power of the local computer. When encountering more complex scene situations, local hardware often becomes a bottleneck, causing rendering to take a long time, which in turn has a serious impact on the progress of the project.
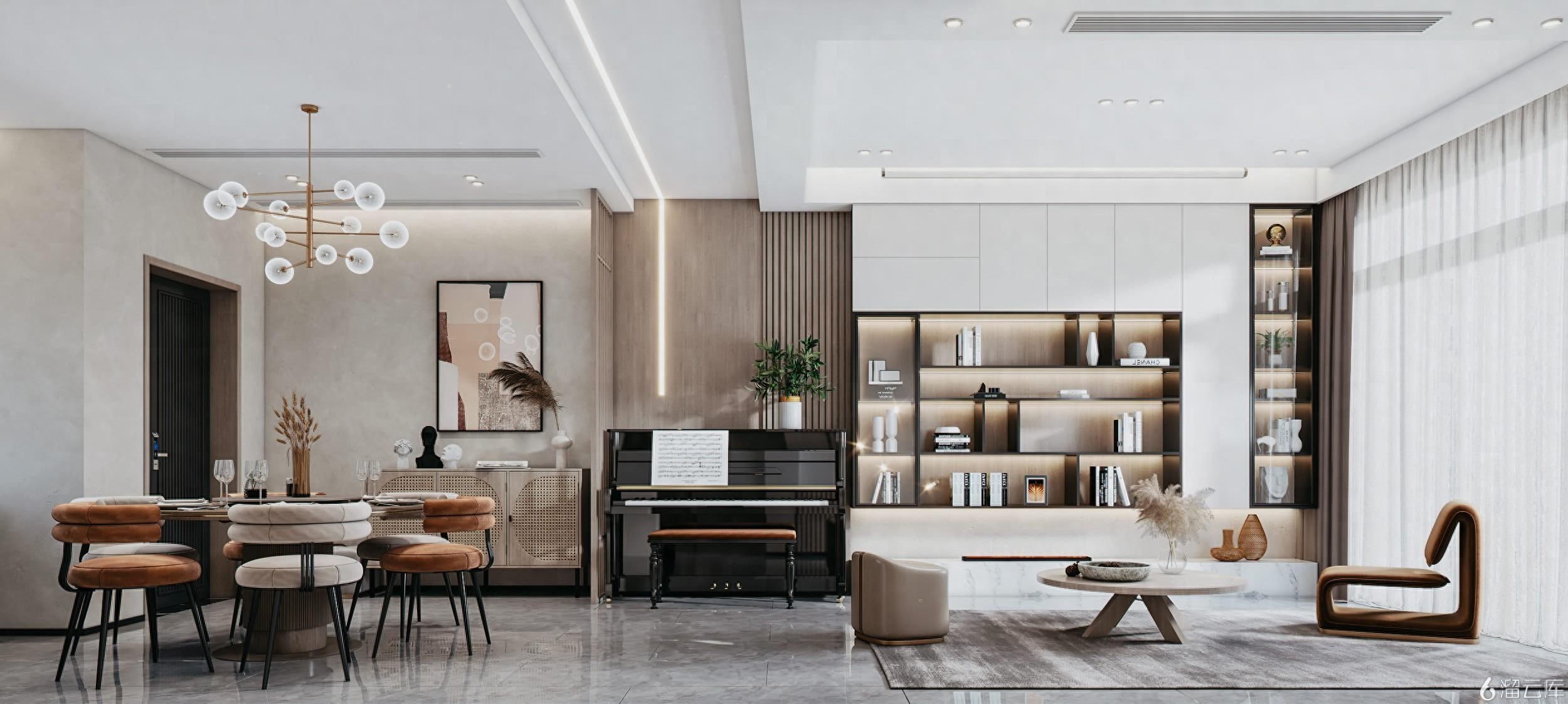

The computing tasks are transferred to the cloud server cluster with the help of cloud rendering technology. Designers only need to upload project files, and the high-performance servers in the cloud will take over all the complex computing work and return the results after completing the relevant work. This process frees up local resources.
Significant improvements in efficiency and quality
The most intuitive benefit of using cloud rendering is the rapid improvement of efficiency. An animation frame that takes dozens of hours to complete locally may only take dozens of minutes in the cloud. This speed advantage is extremely critical when the project cycle is tight.
In addition to speed, the professional hardware configuration of the cloud server also plays a role in ensuring higher rendering quality. They are generally equipped with top-level GPUs and large memories, which can handle more complex ray tracing and global illumination calculations, thereby outputting results with more delicate image quality.
Innovation in work models and convenience in collaboration
What promotes the innovation of work models is cloud rendering technology. Designers are no longer bound to a certain high-performance workstation. As long as they can connect to the Internet, they can submit and monitor rendering tasks, achieving freedom of work location.
At the same time, collaboration between teams has become more convenient. Project-related files are stored uniformly in the cloud. Team members can access the latest version at any time and conduct rendering tests. This ensures the consistency of design standards and the smoothness of the process.
Wide range of industry application scenarios
Within the scope of architecture and interior design, cloud rendering is widely used to generate renderings, panoramas, and virtual tours. It can quickly display the effects of different materials and lighting schemes to help customers make decisions.
Another great use case for cloud rendering is in film, television, animation and game development. These industries have extremely high requirements for the realism of the picture and the details of the picture. The rendering volume is huge, and the cloud rendering platform can flexibly call up massive computing resources to meet their demanding production needs.
Features of related software tools
In the current market, there are many software that can provide cloud rendering services. Generally speaking, these software require users to install a client device locally. The device has functions for organizing projects, setting parameters, and uploading files. This client is designed with an emphasis on simplicity and ease of use.
The key functions of these software are not much different, mainly around task management. Users can create a rendering queue in the client, select the rendering server configuration, set the image format and resolution, and view the rendering progress and estimated completion time in real time.
Factors to consider when choosing a cloud rendering service
When choosing a specific cloud rendering service, price is the primary factor that needs to be considered. Many platforms use a pay-as-you-go billing model. Users have to estimate costs based on parameters such as rendering time and number of cores used to find the most cost-effective solution.
Software compatibility is as key as technical support. An excellent service provider must be able to support the mainstream DCC software versions and renderer versions in the industry, and must provide timely technical responses to help users solve various problems encountered during the rendering process.
Nowadays, more and more design companies are beginning to incorporate cloud rendering into the standard workflow category. Have you ever used cloud rendering technology in your own projects? Is the most significant change it brings to you, saving time or improving the quality of your work? Welcome to share your real experience in the comment area.